배경
RubiyaLab CTF팀으로 BrunnerCTF 2025에 참여하게 되었습니다.
기간 : 2025-08-22 21:00 ~ 2025-08-24 21:00 (KST)
문제 목록
푼 순서대로
Bake and Forth-Reverse Engineering 점수 - 618점, 푼 팀 - 32/1158팀Un-Pirateable Baking Game-Reverse Engineering 점수 - 365점, 푼 팀 - 50/1158팀Un-Pirateable Baking Game 2-Reverse Engineering 점수 - 966점, 푼 팀 - 5/1158팀 First BloodBake to the Future-Reverse Engineering 점수 - 938점, 푼 팀 - 8/1158팀 First BloodThe Cinnamon Packet-Forensics 점수 - 847점, 푼 팀 - 16/1158팀
Unsolved
The Real Windows Experience-Forensics 점수 - 1000점, 푼 팀 - 1/1158팀
Bake and Forth
문제 상황
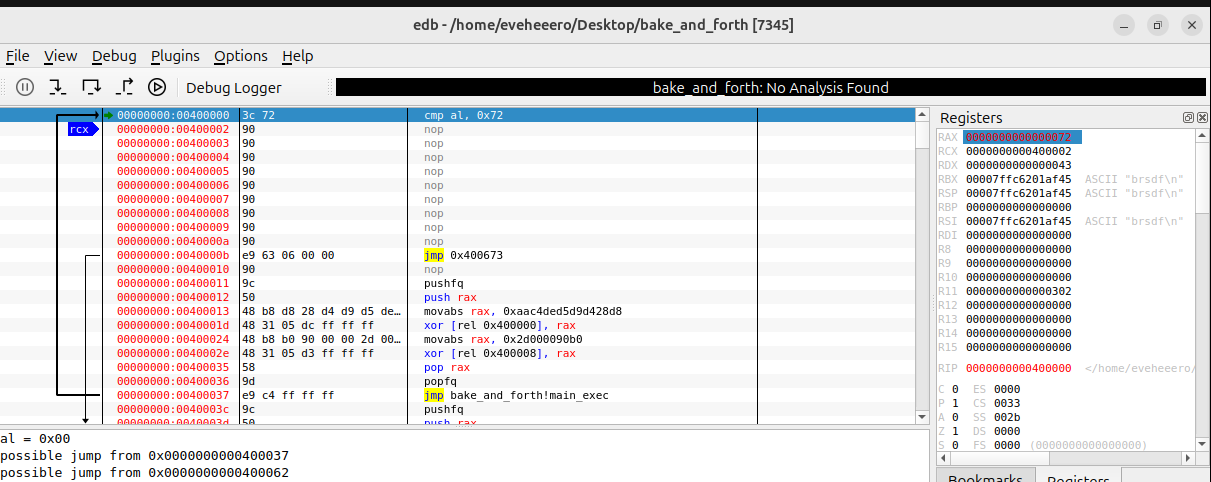
위와 같은 프로그램이 주어졌으며, 0x40000b에서는 항상 0x400000의 인스트럭션을 수정하는 코드로 점프하는 프로그램이었습니다.
분석 과정
0x400000에 브레이크포인트를 걸면 해당 바이트가 인터럽트로 바뀌어, 코드 패치가 오류가 났었습니다.
심심해서 한 줄씩 넘겨가면서 풀었습니다.
한 글자씩 비교하는 프로그램이었습니다.
한 글자씩 비교하다가, 글자 수가 너무 길어서 xor에 영향이 없는 0x40000b에 브레이크포인트를 걸고 진행했습니다.
0x40000b에 항상 jmp 주소인스트럭션이 왔기 떄문에, 0x40000b바이트는 항상 e9로 고정이었습니다.
풀이
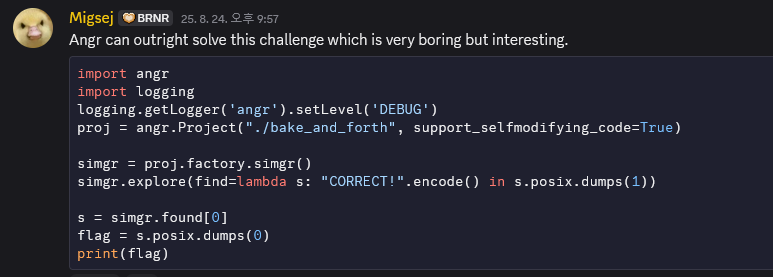
angr을 이용해 자동 분석을 할 수 있다고 합니다.
출제자분은 디스어셈블 + 파이썬을 통해 직접 연산 스크립트를 작성하는것을 계획했다고 합니다.
Un-Pirateable Baking Game
문제 상황
GameMaker로 만든 게임이 주어졌습니다.

게임 실행 시 라이선스 코드를 입력하는 창이 뜹니다.
분석 과정
여러 언패킹 툴을 찾아보았습니다.
UndertaleModTool이 적용되는 언패킹 툴이었습니다.
라이선스 관련 스크립트를 지운 후, data.wim파일을 수정해 적용하려 하였으나, 적용 관련 내용을 찾진 못했습니다.
스크립트를 좀 더 찾아보니 출력 스크립트가 있어 플래그를 알아냈습니다.
draw_set_color(c_white);
draw_set_alpha(1);
draw_set_halign(fa_center);
draw_set_valign(fa_middle);
draw_set_font(HeadlineFont);
draw_text(640, 360, "You baked a cake");
var message = "";
if (!global.isPirated)
{
message = "And it tasted great!";
}
else
{
message = "But you used salt instead of sugar...\nIt's terrible...";
}
draw_set_font(DefaultFont);
draw_text(640, 420, message);
if (!global.isPirated)
{
var f = "";
var a = [72, 88, 95, 68, 68, 79, 88, 81, 68, 26, 117, 93, 30, 83, 11, 117, 94, 66, 27, 89, 117, 89, 66, 26, 70, 78, 117, 66, 30, 92, 25, 117, 72, 25, 25, 68, 117, 27, 71, 90, 26, 89, 89, 27, 72, 70, 25, 87];
for (var i = 0; i < 48; i++)
{
f += chr(a[i] ^ 42);
}
draw_text(640, 450, f);
}
Un-Pirateable Baking Game 2
문제 상황
Un-Pirateable Baking Game와 비슷해보이지만, 스크립트가 YYC (YoYoCompiler)에 의해 컴파일되어 바이너리로 들어갔다고 합니다.
brunnerctf\rev_un-pirateable-baking-game-2\UTMT_CLI_v0.8.3.0-Windows>UndertaleModCli.exe dump ..\data.win -o ..\dump -c UMT_DUMP_ALL
Trying to load file: 'brunnerctf\rev_un-pirateable-baking-game-2\data.win'
The game was made with YYC (YoYo Compiler), which means that the code was compiled into the executable. There is thus no code to dump. Exiting.
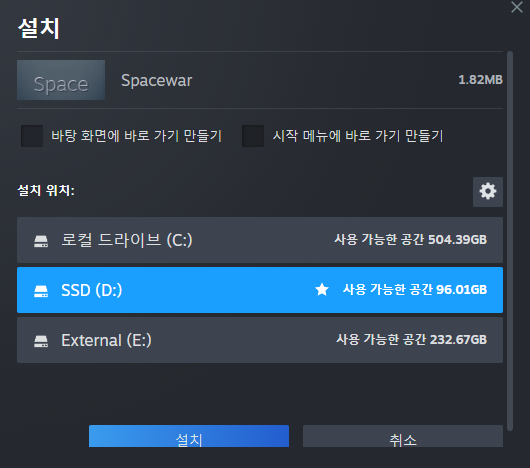
실행 시 스팀 클라이언트가 켜지며, spacewar게임을 설치하려 합니다.
관련 게임을 살펴보니, 밸브의 오래된 게임이었습니다.
분석 과정

Un-Pirateable Baking Game의 플래그 출력 스크립트에 나온 문자열을 기준으로 검색해보니, 같은 문자열이 나왔습니다.
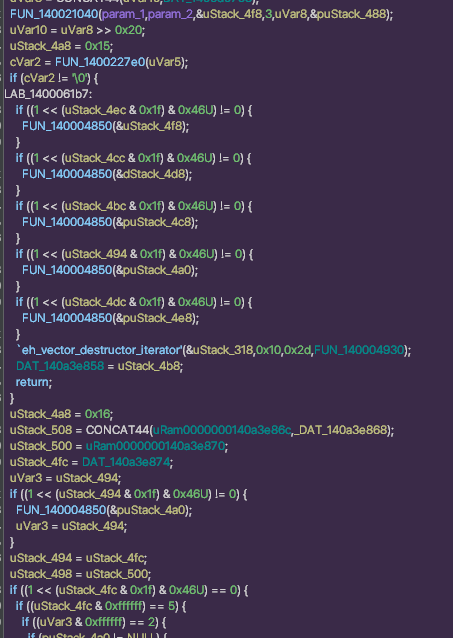
문자열에 대해 xref를 잘 찾아보니 복잡한 함수가 나왔습니다.
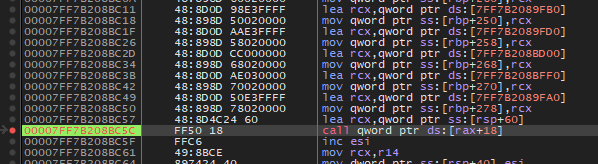

게임에 디버거를 붙여 실행한 후 한 줄씩 실행하며 스팀 관련 초기화 함수를 찾아 우회했습니다.

똑같은 화면이 뜨며 라이선스 코드를 검사합니다. 지난번 스크립트를 보면 스팀id등을 비교했기 때문에, 어떤 값을 입력하더라도 패스는 불가능합니다.
프로그램 내부 문자열중 의미심장한곳을 찾아 브레이크포인트를 걸면, 같은 위치에서 루프를 걸어가면서 모든 함수를 호출하는것을 볼 수 있습니다.
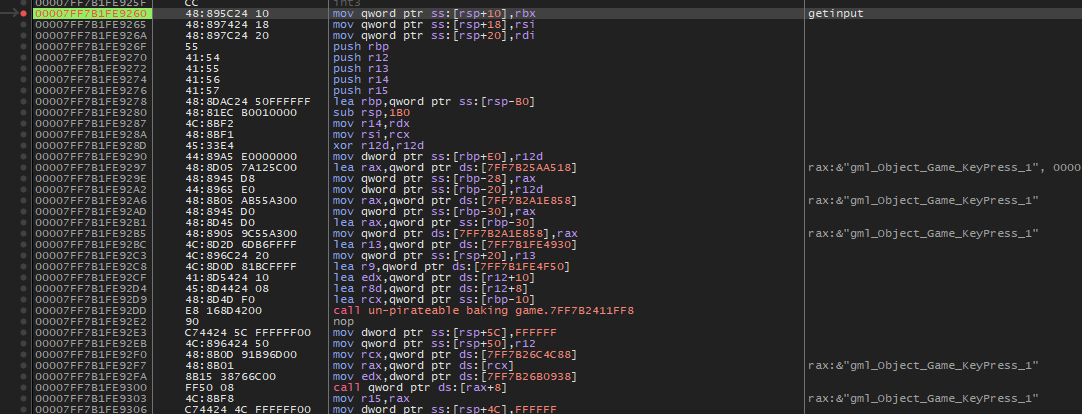
의미심장한 함수 예시이며, gml_Object_Game_KeyPress_1이라는 문자열을 사용하고 있었습니다. 라이선스 키 입력받는 함수였습니다. |
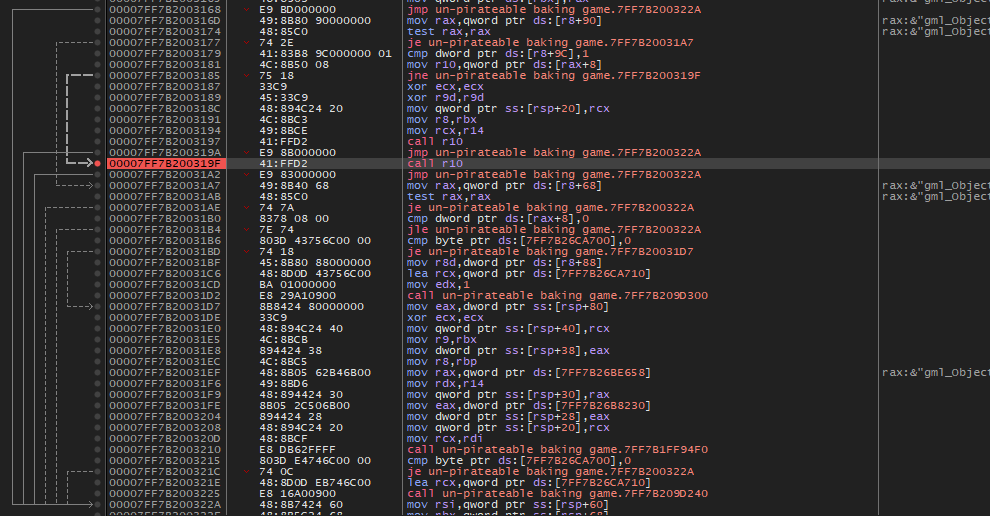
| 다음 위치에서 비슷한 함수들을 호출하고 있었습니다. |
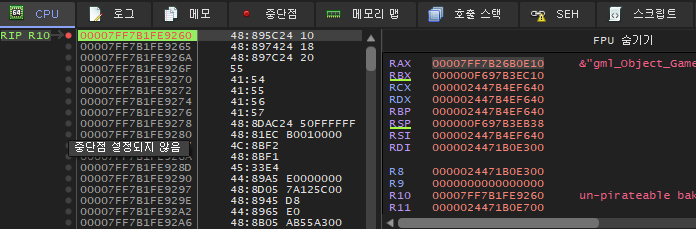
함수 시작 위치에서 잘 보면 rax가 스크립트 이름, r10이 함수 위치로 설정된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
플래그 출력하는 함수의 시작 부분으로 rip를 옮긴 후, rax와 r10을 조절하면 플래그 출력이 이루어집니다. (일부 조건은 우회해야합니다.)
Un-Pirateable Baking Game에서 얻은 플래그 출력 함수인 gml_Object_End_Draw_64를 기준으로 함수를 찾아, rip, rax, r10을 수정합니다. (사실 rax는 함수 시작 후 바로 덮어써지므로 수정하지 않아도 됩니다.)
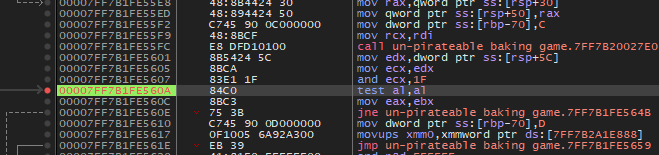
계속 진행하다보면 기존 스크립트처럼 분기가 몇 개 있는데, 시행착오를 거쳐가면서 수정할 지점을 알아가면 됩니다. | 분기는 560a 및 57c2에 있습니다.
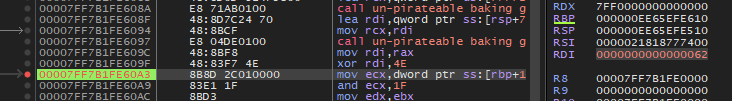
기존 로직의 xor을 키워드로 계속 넘어가다보면, 한 글자씩 문자열을 복호화하는 부분을 찾을 수 있습니다.
Bake to the Future
문제 상황
Bake and Forth와 비슷한 문제이나, 단순한 로직이 아닌 복잡한 로직이 들어있었습니다.
분석 과정
(gdb) b *0x40000b
Breakpoint 1 at 0x40000b
(gdb) commands
Type commands for breakpoint(s) 1, one per line.
End with a line saying just "end".
>silent
>x/i 0x400000
>continue
>end
위 스크립트로 어셈블리를 뽑아냈습니다.
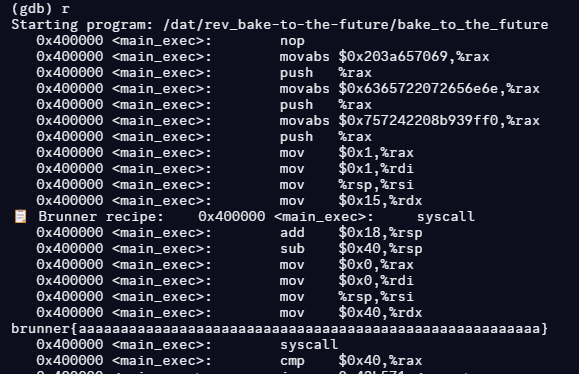
정규식을 통해 보기 쉽게 다듬은 후, gpt를 돌렸습니다.

AES 일부 라운드만을 돌려주는 프로그램이라고 합니다.
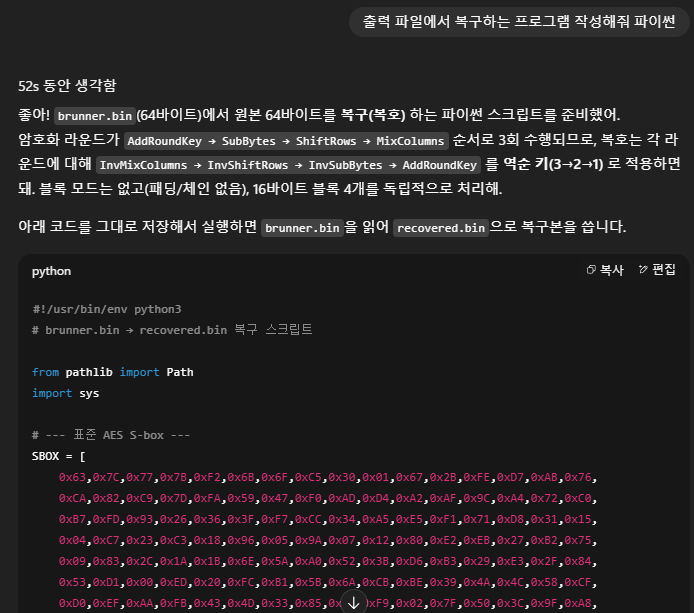
# brunner.bin → recovered.bin 복구 스크립트
from pathlib import Path
import sys
# --- 표준 AES S-box ---
SBOX = [
0x63,0x7C,0x77,0x7B,0xF2,0x6B,0x6F,0xC5,0x30,0x01,0x67,0x2B,0xFE,0xD7,0xAB,0x76,
0xCA,0x82,0xC9,0x7D,0xFA,0x59,0x47,0xF0,0xAD,0xD4,0xA2,0xAF,0x9C,0xA4,0x72,0xC0,
0xB7,0xFD,0x93,0x26,0x36,0x3F,0xF7,0xCC,0x34,0xA5,0xE5,0xF1,0x71,0xD8,0x31,0x15,
0x04,0xC7,0x23,0xC3,0x18,0x96,0x05,0x9A,0x07,0x12,0x80,0xE2,0xEB,0x27,0xB2,0x75,
0x09,0x83,0x2C,0x1A,0x1B,0x6E,0x5A,0xA0,0x52,0x3B,0xD6,0xB3,0x29,0xE3,0x2F,0x84,
0x53,0xD1,0x00,0xED,0x20,0xFC,0xB1,0x5B,0x6A,0xCB,0xBE,0x39,0x4A,0x4C,0x58,0xCF,
0xD0,0xEF,0xAA,0xFB,0x43,0x4D,0x33,0x85,0x45,0xF9,0x02,0x7F,0x50,0x3C,0x9F,0xA8,
0x51,0xA3,0x40,0x8F,0x92,0x9D,0x38,0xF5,0xBC,0xB6,0xDA,0x21,0x10,0xFF,0xF3,0xD2,
0xCD,0x0C,0x13,0xEC,0x5F,0x97,0x44,0x17,0xC4,0xA7,0x7E,0x3D,0x64,0x5D,0x19,0x73,
0x60,0x81,0x4F,0xDC,0x22,0x2A,0x90,0x88,0x46,0xEE,0xB8,0x14,0xDE,0x5E,0x0B,0xDB,
0xE0,0x32,0x3A,0x0A,0x49,0x06,0x24,0x5C,0xC2,0xD3,0xAC,0x62,0x91,0x95,0xE4,0x79,
0xE7,0xC8,0x37,0x6D,0x8D,0xD5,0x4E,0xA9,0x6C,0x56,0xF4,0xEA,0x65,0x7A,0xAE,0x08,
0xBA,0x78,0x25,0x2E,0x1C,0xA6,0xB4,0xC6,0xE8,0xDD,0x74,0x1F,0x4B,0xBD,0x8B,0x8A,
0x70,0x3E,0xB5,0x66,0x48,0x03,0xF6,0x0E,0x61,0x35,0x57,0xB9,0x86,0xC1,0x1D,0x9E,
0xE1,0xF8,0x98,0x11,0x69,0xD9,0x8E,0x94,0x9B,0x1E,0x87,0xE9,0xCE,0x55,0x28,0xDF,
0x8C,0xA1,0x89,0x0D,0xBF,0xE6,0x42,0x68,0x41,0x99,0x2D,0x0F,0xB0,0x54,0xBB,0x16,
]
# InvSBox는 SBOX의 역함수
INV_SBOX = [0]*256
for i, v in enumerate(SBOX):
INV_SBOX[v] = i
def add_round_key(s: bytes, k: bytes) -> bytes:
return bytes(a ^ b for a, b in zip(s, k))
def sub_bytes(s: bytes) -> bytes:
return bytes(SBOX[b] for b in s)
def inv_sub_bytes(s: bytes) -> bytes:
return bytes(INV_SBOX[b] for b in s)
def shift_rows(s: bytes) -> bytes:
# column-major: r0=[0,4,8,12], r1=[1,5,9,13], r2=[2,6,10,14], r3=[3,7,11,15]
s = list(s)
r0 = [s[0], s[4], s[8], s[12]]
r1 = [s[1], s[5], s[9], s[13]]
r2 = [s[2], s[6], s[10], s[14]]
r3 = [s[3], s[7], s[11], s[15]]
def rot_left(x,n): n%=4; return x[n:]+x[:n]
r0, r1, r2, r3 = rot_left(r0,0), rot_left(r1,1), rot_left(r2,2), rot_left(r3,3)
out = [0]*16
out[0], out[4], out[8], out[12] = r0
out[1], out[5], out[9], out[13] = r1
out[2], out[6], out[10], out[14] = r2
out[3], out[7], out[11], out[15] = r3
return bytes(out)
def inv_shift_rows(s: bytes) -> bytes:
# 오른쪽 순환(역방향)
s = list(s)
r0 = [s[0], s[4], s[8], s[12]]
r1 = [s[1], s[5], s[9], s[13]]
r2 = [s[2], s[6], s[10], s[14]]
r3 = [s[3], s[7], s[11], s[15]]
def rot_right(x,n): n%=4; return x[-n:]+x[:-n] if n else x
r0, r1, r2, r3 = rot_right(r0,0), rot_right(r1,1), rot_right(r2,2), rot_right(r3,3)
out = [0]*16
out[0], out[4], out[8], out[12] = r0
out[1], out[5], out[9], out[13] = r1
out[2], out[6], out[10], out[14] = r2
out[3], out[7], out[11], out[15] = r3
return bytes(out)
def gf_mul(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""GF(2^8), 모듈러스 x^8+x^4+x^3+x+1 (0x11B)"""
res = 0
for _ in range(8):
if b & 1:
res ^= a
hi = a & 0x80
a = ((a << 1) & 0xFF)
if hi:
a ^= 0x1B
b >>= 1
return res
def mix_columns(s: bytes) -> bytes:
s = list(s)
out = [0]*16
for c in range(4):
i = 4*c
a0,a1,a2,a3 = s[i],s[i+1],s[i+2],s[i+3]
out[i+0] = gf_mul(a0,2) ^ gf_mul(a1,3) ^ a2 ^ a3
out[i+1] = a0 ^ gf_mul(a1,2) ^ gf_mul(a2,3) ^ a3
out[i+2] = a0 ^ a1 ^ gf_mul(a2,2) ^ gf_mul(a3,3)
out[i+3] = gf_mul(a0,3) ^ a1 ^ a2 ^ gf_mul(a3,2)
return bytes(out)
def inv_mix_columns(s: bytes) -> bytes:
s = list(s)
out = [0]*16
for c in range(4):
i = 4*c
a0,a1,a2,a3 = s[i],s[i+1],s[i+2],s[i+3]
out[i+0] = gf_mul(a0,0x0e) ^ gf_mul(a1,0x0b) ^ gf_mul(a2,0x0d) ^ gf_mul(a3,0x09)
out[i+1] = gf_mul(a0,0x09) ^ gf_mul(a1,0x0e) ^ gf_mul(a2,0x0b) ^ gf_mul(a3,0x0d)
out[i+2] = gf_mul(a0,0x0d) ^ gf_mul(a1,0x09) ^ gf_mul(a2,0x0e) ^ gf_mul(a3,0x0b)
out[i+3] = gf_mul(a0,0x0b) ^ gf_mul(a1,0x0d) ^ gf_mul(a2,0x09) ^ gf_mul(a3,0x0e)
return bytes(out)
# --- 고정 라운드키 (ASCII 그대로 16바이트) ---
RK = [
b"One_DoughLorean_", # round 1
b"MartyMcPie_With_", # round 2
b"Doc_Brown_Sugar!", # round 3
]
assert all(len(k)==16 for k in RK)
def decrypt_block(ct: bytes) -> bytes:
"""한 블록(16B) 복구"""
s = ct
# round 3 → 2 → 1
for rk in (RK[2], RK[1], RK[0]):
s = inv_mix_columns(s)
s = inv_shift_rows(s)
s = inv_sub_bytes(s)
s = add_round_key(s, rk)
return s
def decrypt_file(in_path: Path, out_path: Path):
data = in_path.read_bytes()
if len(data) % 16 != 0:
raise ValueError(f"입력 길이가 16의 배수가 아님: {len(data)} bytes")
out = bytearray()
for off in range(0, len(data), 16):
out += decrypt_block(data[off:off+16])
out_path.write_bytes(bytes(out))
print(f"[+] 복구 완료: {out_path} ({len(out)} bytes)")
# 보기 좋게 일부 출력
try:
txt = bytes(out).decode("utf-8")
print("[*] UTF-8로 해석한 내용(일부):")
print(txt if len(txt)<=200 else txt[:200]+"...")
except Exception:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
in_file = Path(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) > 1 else Path("brunner.bin")
out_file = Path(sys.argv[2]) if len(sys.argv) > 2 else Path("recovered.bin")
decrypt_file(in_file, out_file)
The Cinnamon Packet
문제 상황
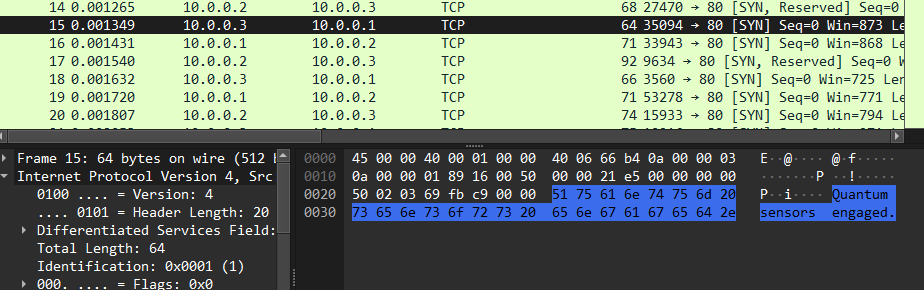
알 수 없는 패킷을 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1로 돌아가면서 보내고 있었습니다.
분석 과정
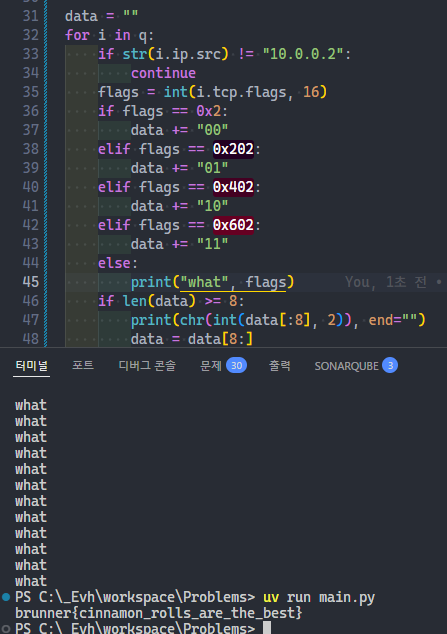
for index, i in enumerate(q):
line = ""
line += chr(int(i.tcp.srcport, 16) >> 8)
line += chr(int(i.tcp.srcport, 16) & 0xFF)
line += chr(int(i.tcp.checksum, 16) >> 8)
line += chr(int(i.tcp.checksum, 16) & 0xFF)
line += chr(int(i.tcp.window_size, 16) & 0xFF)
line += chr(int(i.tcp.len))
line += chr(int(i.tcp.seq_raw, 16) >> 8)
line += chr(int(i.tcp.seq_raw, 16) & 0xFF)
line += "".join(
[
chr(int(i.tcp.segment_data[x : x + 2], 16))
for x in range(0, len(i.tcp.segment_data), 3)
]
)
if "{" in line:
print(index)
pyshark를 통해 여러 패킷을 다양한 필터링을 걸고, 다양하게 복호화 했으나 플래그가 나오지 않았습니다.
계속 보다 보니, 10.0.0.2가 보낸 패킷의 tcp.flags 일부가 0x002, 0x202, 0x402, 0x602로 표시되는것을 보았습니다.
0x002 -> 00, 0x202 -> 01, 0x402 -> 10, 0x602 -> 11로 변환하여 풀 수 있었습니다.
The Real Windows Experience
문제 상황
리눅스를 윈도우처럼 쓰는 사람이 바이러스에 걸렸다고 합니다. 내용을 보니 wine프로그램으로 프로그램을 사용하던 중 바이러스에 걸렸습니다.
분석 과정
다운로드에 애플뮤직 인스톨러가 있어 바이러스토탈에 돌려보니 바이러스 의심이라는 내용의 코멘트가 있었습니다.
관련해서 살펴봤는데 아무것도 나오지 않았었습니다.
wine내부 파일들을 전부 분석했지만 별 내용이 없었습니다.
알고보니 파일 카빙을 진행하는거라고 합니다.
풀이
- Find the encrypted DOCX file in Documents.
- Find update.exe mentioned in the recently-used.xbel (/home/oliver/.local/share/recently-used.xbel) file. It’s the malware and has been run with Wine.
- Find the only carved .exe file in the volume using Autopsy, this is the malware - it’s not present in the filesystem anywhere.
- Notice that the update.exe that most carving tools get is a pain to reverse, leading to the hint in the description. Find the file in the raw disk dump with a hexeditor. See that the file is actually a lot longer in the raw disk dump and dump the entire file. If not you loose all symbols.
- Reverse the update.exe file, written in Nim, to understand that it creates a key using epochtime hashed with SHA-256 and AES encrypts the file.
- Epoch time is 1754665142
- Key is then 0ba2721f8aa3dfa0dabb894077fa7394a0f05150e9cee8546be3e2a9eeba5288
- Either find hardcoded IV or discover that it is prepended to the file.
- IV is 04a51607f00142030c0dbe0f08092a5b
- Create decrypter and use timestamp of .enc file creation. The timestamp is converted to hex (upper case) and left padded with 0s until 16 bytes long, before being hashed.
작성자의 글
- .
참조
- .
